GPS Radio Occultation

Global Positioning System (GPS) Radio Occultation (RO) senses the atmosphere using GPS radio signals that traverse the atmosphere as a moving receiver sets behind the horizon relative to the transmitting satellite. The radio raypath is refracted (bend) and its travel time is delayed due to variations of refractivity (Fig. 1). Precise measurements of the phase delay can reveal high vertical resolution structure of atmospheric bending and refractivity, from which one can then derive atmospheric quantities such as air density, pressure, geopotential heights, temperature and moisture.
The refractivity, N (N = (n-1) × 10^6, where n is the refractive index) at GPS frequency (f), is related to the atmospheric pressure (P in mbar), temperature (T in Kelvin), and water vapor partial pressure (Pw in mbar) in the neutral atmosphere as well as the ion density (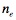 ) through Smith and Weintraub (1953).
) through Smith and Weintraub (1953).
Ionosphere
Neutral Atmosphere
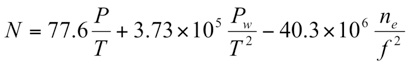
Courtesy of UCAR COSMIC